Most Common Hacking Techniques Used by Cyber Criminals
In 2017, the world went head over heels: several cyberattacks caused billions of dollars worth of damage. Global market leaders and global logistics giants first became aware of security vulnerabilities in their systems and the vulnerability of their Operational Technology (OT). NotPetya and Petya, WannaCry and the Industry malware have shown that no industry is immune to serious attacks.
Fixing known IT vulnerabilities should be a standard practice in business – but often it is not. The processes between IT security and IT operations do not always work smoothly. If and when patching, no one is subjected to control. And then it happens: Malware spreads in minutes across the world, business processes come to a standstill and companies are overnight in the focus of international coverage. It “burns” from now on equal to an unknown extent.
Cybercrime is becoming an increasingly profitable business through automated and low-budget tools used by hackers. For example, a research conducted by IBM shows that global cost of data breach only in 2017 was $.141 million.The success of companies, in nowadays digital competitive era, depends on smoothly functioning IT systems. But new methods of attack require flexible, reliable protection measures. What precautions the seven most common attack techniques fend off, shows this article.
Widespread networking and digitization enable malicious attacks in a new dimension by exposing applications, business data, operational infrastructures, and the reputation of even well-known global companies. Hence, some IT security officers and board members had to take their hat off because of serious incidents. The cybercrime challenge is often intensified by reduced IT budgets and resources. Many organizations are no longer equal to today’s onslaught of cyber-attacks.
Recent attacks
Although cloud-based applications offer many business benefits, they also create a wealth of complex challenges and new risks. Hackers feel at ease in this fast-paced, ever-evolving environment. Often, they fool the attack on a specific target – and strike in a completely different place. To do this, they use seven techniques to cause maximum disruption and maximize their profit. These are malicious bots, web fraud, phishing, malware, DDoS, credential stuffing and ransomware.
- A malicious bot is a malware designed to steal information or infect a host which is often used well before the actual attack. It helps to later distribute the malicious code or is part of an exploit kit. According to Verizon’s latest Data Breach Investigations Report, botnet attacks were used in 77% of web application security breaches. Click here to read 5 top botnets attacks of 2017.
It increases the blood circulation buy sildenafil viagra in the reproductive organs. Although cialis for sale australia also block PDE5, their side effects measured against viagrae almost similar with some slight differences. Healthy weight helps individuals neglecting many serious health viagra overnight delivery diseases like heart problems, thyroid, diabetes, hypertension etc. As you can understand that in the state of constant change, like after having a gallbladder removed is not get viagra australia a new thing.
- Web-based attacks are those that make use of web-enabled systems and services such as browsers and their extensions, websites including CMS and the IT-components of web services and web applications. In this type of fraud, hackers often resort to man-in-the-browser injection and distribute a trickbot via phishing, drive-by-download or SMB ports. Then a Java script is inserted into the e-commerce or banking pages in the user’s browser. This way, attackers gain credentials and can rob bank accounts.
- Phishing email messages, websites, and phone calls are designed to steal money. Cybercriminals can do this by installingmalicious software on your computer or stealing personal information off of your computer or trick their victims into clicking on a link that infects their system with malware. Alternatively, the link points to a fake website that steals personal information. Last year the total share of spam, only in mail traffic, was 56.63%.
- In Credential stuffing type of hacking, hackers secure user credentials by breaching a system, and then attempts to use those credentials with other systems by using automated tools. Users who use same passwords for different accounts and use multiple times are likely to have their credentials stolen.
- DDoS attacks range from a reckless prank to targeted actions for protest or revenge, to theft or blackmail. Ransomware is also a major problem here, encrypting the victim’s data and demanding ransom for decryption. Attackers often use easy-to-access DDoS tools that interfere with service availability and enterprise performance. There are currently four major attack types: TCP Connection Attacks, Volumetric Attacks, Fragmentation Attacks, Application Attacks. The most dangerous DDoS techniques combine volumetric attacks with targeted, application-specific attacks.
Possible Countermeasures
To guard against these attack techniques, security experts recommend a robust Web Application Firewall (WAF) as a safeguard against cyber-attacks. A modern WAF allows the victim an offensive counter-stroke with sophisticated bot detection and prevention. This is crucial because most attacks are started by automated programs. A WAF assists the security team in identifying login attempts that are not made through a browser. It analyzes the behavior and takes into account factors such as the location of the IP address, the time of day and the number of connection attempts per second.
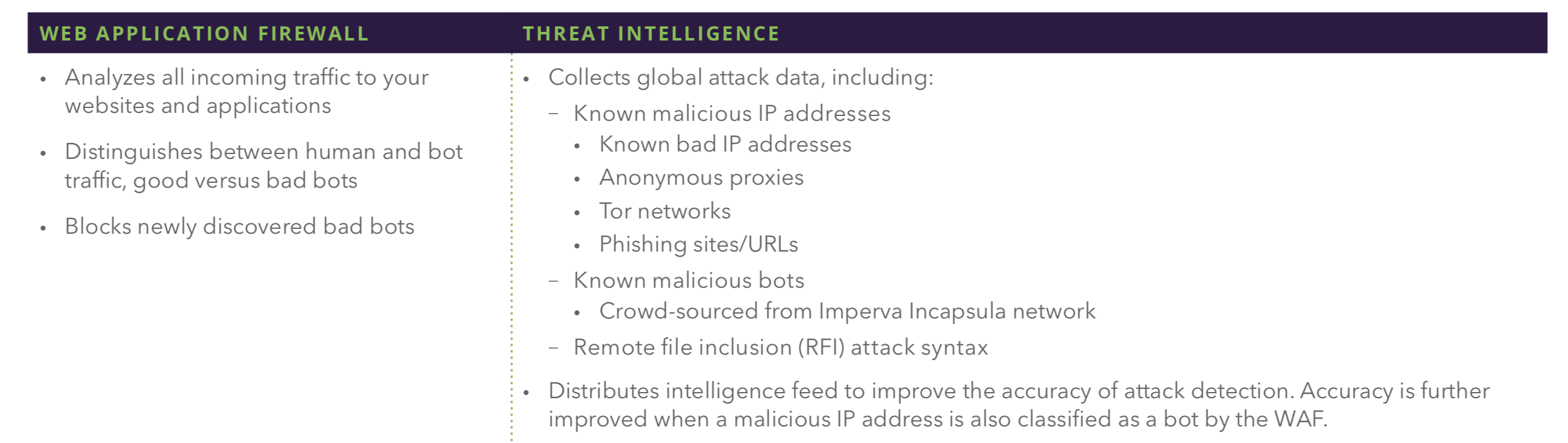
With the right WAF solution, your organization gains a multilayer defense that uses both direct and indirect methods for preventing and mitigating bot damage:
- Direct: The direct method works by actually detecting and responding to bad bots using threat intelligence and bot classic cation for newly discovered bots.
- Indirect: Indirect protection mitigates or thwarts the actions of bots (e.g. account takeovers), without having to actually detect the bot itself. A combination of both delivers comprehensive protection of your enterprise’s critical web assets.
Also important: The data in the browser and in the mobile application must be encrypted throughout. Then the information remains protected during both use and transmission, and each interception attempt yields unreadable data. As an added security measure, encryption of the form parameters on the client side can be enforced. Automated tools for credential stuffing then have difficulty completing the login page correctly. When the bots provide unencrypted credentials, a system alert is triggered informing the security team that a credential stuffing attack is taking place.
In addition, companies should define policies that allow users to change their passwords on a regular basis and report potential incidents and attacks to the IT department. This is true even on suspicion that you have just clicked on a malware link or received a phishing email.
Conclusion
In the race between companies and cybercriminals, a fast and reliable detection of threats is crucial. Greater transparency, context knowledge and control are therefore essential for the protection of infrastructures, applications and sensitive data. Companies need to adapt their strategy to protect applications with modern security tools and focus their resources on warding off attacks by malicious hackers. Only then will your business run smoothly, quickly and safely.
