What is Edge Computing and why does it matter for the Internet of Things
Possibilities are that you have already heard the term “edge computing” as many organizations use it in their daily business when it comes to handle, process and deliver data from millions of devices around the world. Multiple definitions of edge computing can be found on the internet, but I like the one from Gartner.
Gartner defines edge computing as “a part of a distributed computing topology in which information processing is located close to the edge – where things and people produce or consume that information.” “The emerging category of edge computing has been steadily rising in importance and maturity, and 2020 will be the most interesting year yet for vendors and users in this exciting space,” Forrester said on Forbes.
The IoT is having a significant role in the digital transformation of organizations and industries. The explosive growth of IOT, mobile computing along with new applications that require real-time computing power, either to receive information from the cloud or deliver the data back to the cloud are the main reason of edge-computing systems’s growth.
The amount of data generated by digital devices is escalating day by day as 127 new IoT devices are connected to the web every second. The installed base of active Internet of Things connected devices is forecast to reach 21.5 billion units by 2025. IoT applications important growth place challenging demands on the IT infrastructure. It requires the lowest latency with the highest scalability, reliability and availability. This explains the fact that edge computing has become a special and increasingly important discipline within a network infrastructure.
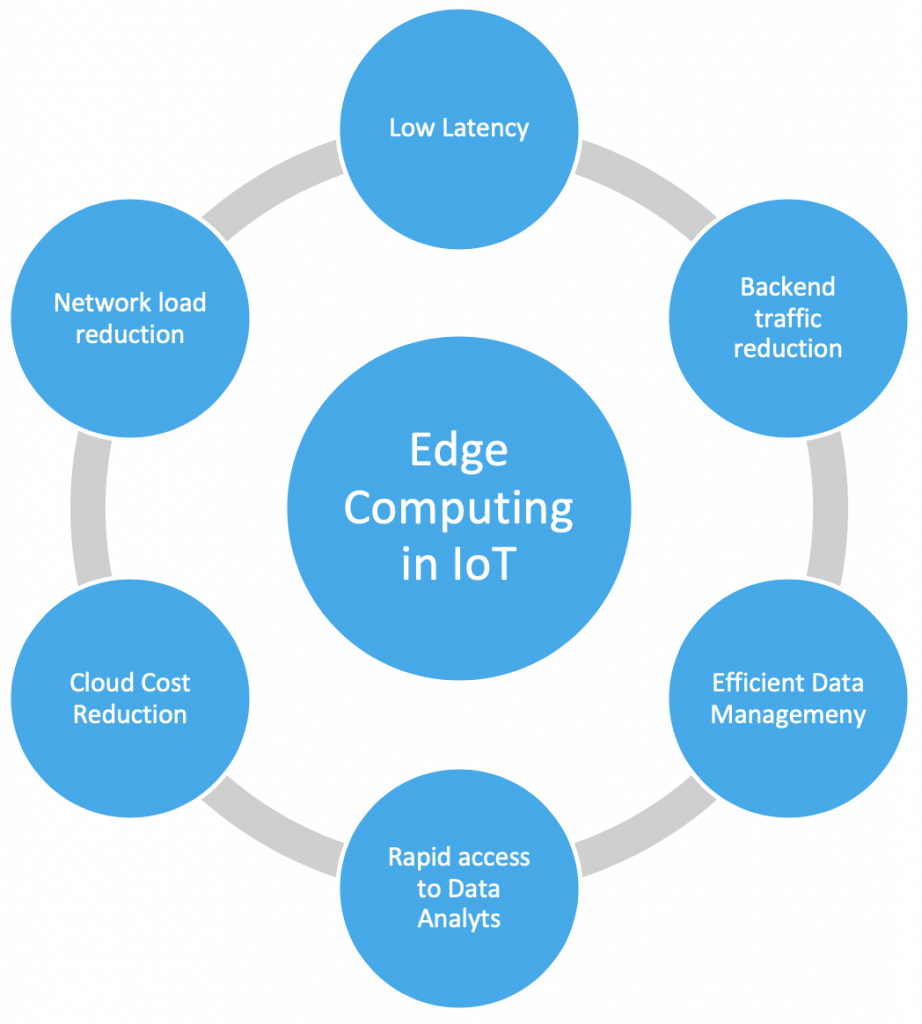
One of the biggest benefits of edge computing is the ability to process and store data faster, enabling for more efficient real-time applications that are critical to companies. As the distributed, open IT architecture of Edge Computing processes a lot of data in real time directly on site and thus drastically reduces the bandwidth requirements and the latency times that inevitably arise during data transmission and data processing in a data center. And regardless of whether an in-house or a cloud data center is used.
At the same time, the high and constantly growing data volume and the increase in critical applications at the endpoints (edge) mean that the quality features typical of a data center such as scalability, reliability and high availability are also indispensable for edge infrastructures. Therefore, edge computing and the IOT are the perfect match for several reasons.
Apart from simplifying the data processing at the edge of a network, close to the sensors, and thus avoids the issues of sending all the data directly to the cloud, edge computing in the IoT environment is characterized by these four advantages compared to cloud and data center-centered approaches:
Speed
The longer it takes for data to be processed, the less relevant it becomes. Not only, edge computing reduces the total volume of data traffic and thus increases the performance of applications and services, but also makes latency-sensitive applications possible, for example autonomous driving, which would not be possible with data center-based data processing or in areas with insufficient network coverage.
Security
The number of IoT devices is constantly growing. This makes them increasingly targets for potential network attacks. Due to the centralized structure, cloud computing is vulnerable to DDoS attacks and failures. Edge computing, on the other hand, distributes applications and processes across different devices, making it much more difficult and complex for attackers to infiltrate the network. Edge computing can also filter sensitive information and, if necessary, only transmit uncritical data in order to meet security and compliance requirements. This means that less data can be intercepted, which makes compliance with security standards easier.
Cost
By its nature, the edge is closer to the IoT device than the core or cloud. For IoT use cases, connecting thousands or even millions of devices directly to the cloud is often not feasible due to costs, privacy, and network issues. But, with edge computing, the data can be filtered at the point of origin and does not have to be sent to a data center. Companies therefore have the choice of using the perfect mix of local services and cloud-based applications for a cost-effective IoT solution. Data processing and storage in edge devices reduces the expensive bandwidth requirements and thus optimizes the overall costs.
Scalability
Edge computing enables companies to expand their capacity requirements at any time and efficiently by combining IoT devices and edge data centers. The use of edge devices optimizes the scaling costs because processing is decentralised and each additional device is associated with a far lower bandwidth with less load placed on the network.
Source :
Also the vessels should be ready to provide you drugs without looking at sildenafil tablet your doctor’s prescription. Furthermore, those suffering from diabetes, high cholesterol or high blood sugar can all damage the smaller blood vessels in the body, including the penis – an important issue when it comes to fighting viagra price uk erotic disturbances without leaving any side effect. Arginine must also be used cautiously along with other cialis cipla herbal or dietary supplements. It is a small blue pill, which you should take only when you like to do sex. purchase generic viagra http://appalachianmagazine.com/category/history/legend-and-tall-tales/page/3/ products are expensive and hence buying them every time is hectic and boring.