#SaaS Software as a Service – Making Strategic choices
Software as a service (SaaS) is the most known branch of cloud computing. It is a delivery model in which applications are hosted and managed in the data center of a service provider, paid for on a subscription basis, and accessed by a browser via an Internet connection. SaaS has become the increasingly popular delivery model for a wide range of business applications. As of 2022, SaaS is worth over $170 billion (Gartner). The SaaS industry has increased in size by around 500% over the past seven years. Therefore, we’ve decided to list, below, the most common advantages and disadvantages of this model.
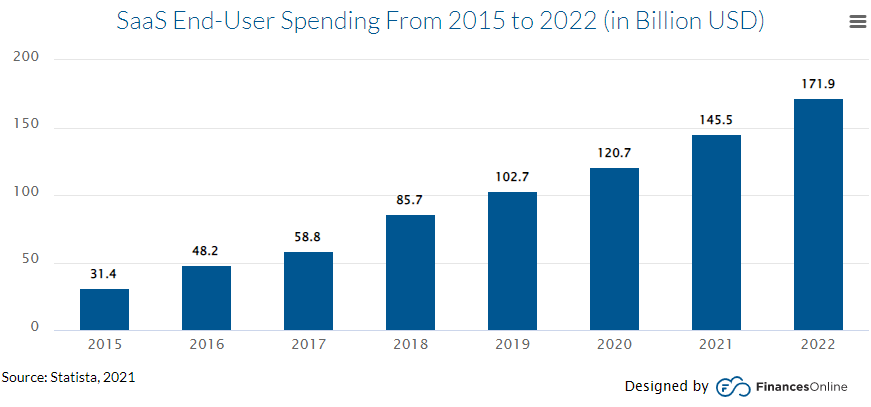
Expression SaaS, used for a decade:
The term “SaaS” for “Software as a Service”, has been commonly used for nearly a decade, while other expressions of cloud computing, such as PaaS – “platform as a service” and IaaS – “Infrastructure as a Service”, are more recent.
Platform as a service (PaaS) refers to the on-demand delivery of software tools and services that enable SaaS applications to be coded and deployed, while an Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) relates to on-demand delivery of operating systems, system maintenance, network capabilities, storage spaces, back-up, and virtualized servers.
An infrastructure hosted in a third-party service provider’s data center is called a “public cloud” infrastructure, while the same technology hosted within a company’s network is referred to as a “private cloud” infrastructure. “Hybrid” cloud environments combine both approaches, with some business processes or workloads remaining in-house, while others (less crucial) are outsourced to public cloud services.
Reason to consider SaaS:
For companies, adopting the SaaS model has many potential benefits, including the following.
- Cost reduction: it is economically very tempting to trade the heavy costs of installing, maintaining, and upgrading an on-site IT infrastructure against the cost of operating a SaaS subscription, including in the short to medium term. However, it is important to be aware of the potential hidden costs associated with adopting SaaS.
- Scalability: As your business grows and you need to add more users, rather than investing in additional software licenses and in-house server capabilities, you can adjust your monthly SaaS subscription as needed.
- Accessibility: in general, a browser and an internet connection are sufficient to access a SaaS application, which can then be made available on various desktops and mobile devices.
- Upgrade capability: Your cloud service provider takes care of software and hardware updates, which frees your internal IT department from a considerable workload (in theory, the teams can be redeployed on different tasks, such as integration with existing on-site applications).
- Resiliency: As the IT infrastructure (and your data) resides in the cloud service provider’s processing center, if your business experiences any kind of disaster, you can become operational again relatively easily from any location equipped with computers connected to the internet.
Arguments against SaaS:
Of course, SaaS also has potential disadvantages, which is why the world has not yet completely switched to the madness of cloud software. Some examples:
- Security: the number one concern for companies considering SaaS is often security: if it is a matter of entrusting sensitive business processes and business data to a third-party service provider, it is essential to address issues such as identity and access management, particularly on mobile devices. If your organization uses multiple cloud services, realize that removing access privileges from a former employee can become a nightmare for security.
- Service interruptions: cloud providers will plan as best they can, service outages are inevitable, whether they are due to a natural disaster, human error, or many intermediate causes. Downtime is always annoying, but a prolonged service interruption can be disastrous when it reaches a critical application. You will need to determine what regulations to apply to your business, ask the right questions to your SaaS provider, and set up a solution to correct any shortcomings.
- Performance: A browser-based application hosted in a remote processing center and accessed via an Internet connection can cause performance concerns over the software running on a local machine or via the company’s local network. Obviously, some tasks will be better suited than others to the SaaS model (at least if the internet speed isn’t a problem). Meanwhile, application performance management tools can help organizations and service providers to monitor how their applications work.
- Data mobility: the SaaS market is teeming with startups, some of which will inevitably fail. What happens to your carefully orchestrated data and business processes if your service provider puts a key on the door or if you need to switch SaaS providers for any other reason?
- Integration: Companies that embrace multiple SaaS applications or want to connect hosted software to existing on-premises applications, are faced with the problem of software integration.
Conclusion
The SaaS market is exploding startups are exploring multiple niches in many software categories, established players acquire and integrate the most promising new services, and brokers in cloud services facilitate the transition of enterprises to the cloud. For new businesses it is virtually self-evident to deploy quickly and pay them through a monthly subscription, rather than investing a generous sum in an on-site IT infrastructure and in-house technical support. The biggest problem faced by small businesses is the huge choice that is already available in the SaaS market.
Large companies have another type of problem to manage when adopting SaaS, focused on integration with existing on-premises enterprise applications (many of which may well be locked by expensive contracts). Still, companies that seek to expand into new regions or adopt new “social” business processes may well consider that SaaS is the most cost-effective way to proceed.
