Cloud Encryption: Best practices to deal with Data Security Issues
For modern businesses, digital transformation is critical, and cloud services offer a proven path to thrive in the digital economy. However, the shared responsibility model states that the cloud service provider is responsible for the security “of” the cloud, while the customer is responsible for the security “in” the cloud, for network controls, identity and access management, application configurations, and, most importantly, data security. Although data in the cloud is often stored abroad, this data storage is the safest option for companies to store files in compliance with the GDPR thanks to end-to-end encryption.
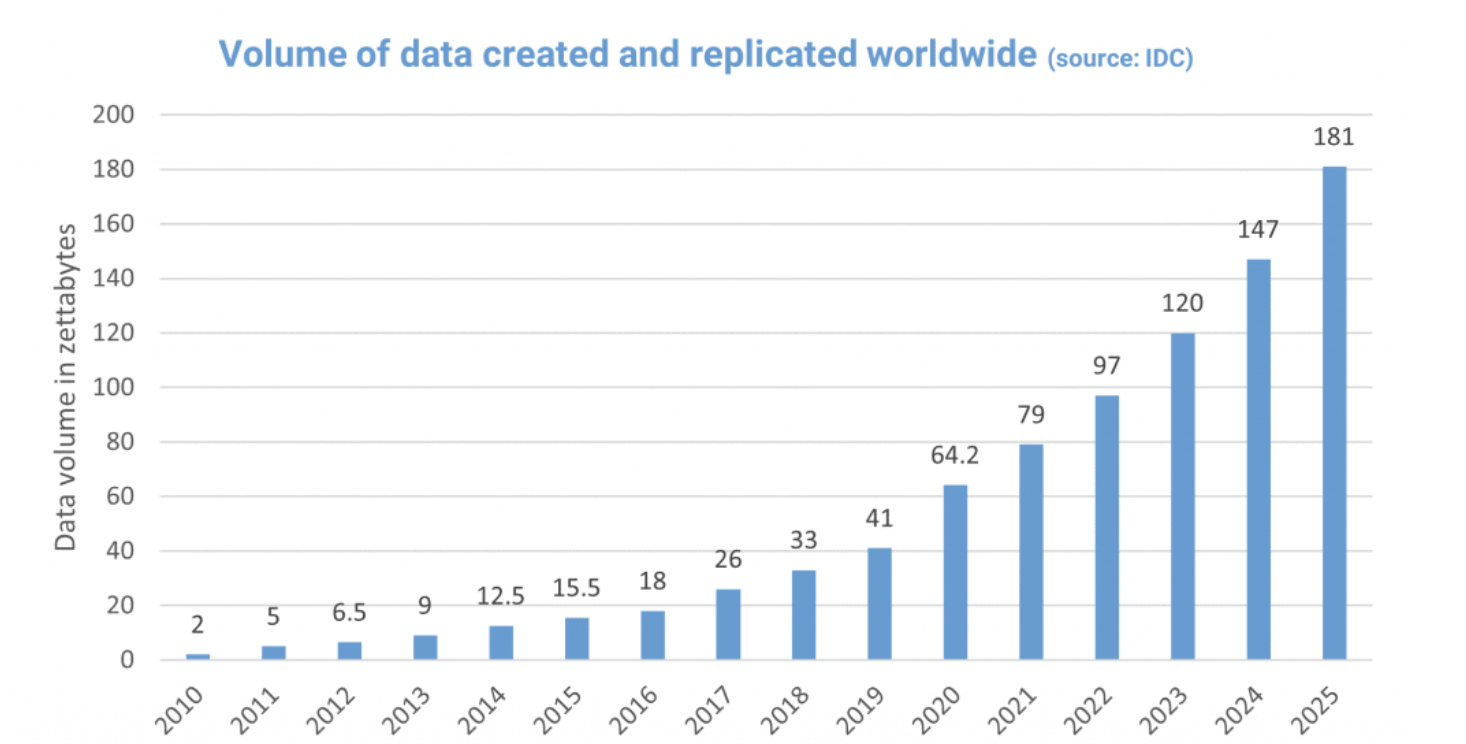
Data is already in the cloud: We all know that growing amounts of data and the desire for flexibility made the cloud increasingly popular as a data storage medium. The advantages are obvious: the files hardly need any local storage space, the cloud is highly available and the data can be accessed from anywhere.
Many programs use the cloud as data storage or backup without the customers being aware of it. This happens when synchronization is set by default or when the program is specially designed for cloud use. This is the case, for example, with Microsoft Office. This is at the root of a serious privacy problem: loss of control. Eventually, information is sent to servers that are beyond the control of whoever owns the data.
Beware of collaboration software: Hesitations about the cloud relate primarily to the lack of data protection. Despite this, too few companies are still taking the initiative. Countermeasures are only slowly being implemented. As a result, the number of data leaks reported to Belgium’s Data Protection Authority, APD, increased significantly every year. “Over the past twelve months, reported cases of breached data have gone up to 1,529,” the newspaper cites APD spokesperson Aurélie Waeterlinckx as saying. “The year before, there were 1,232.” Many companies are aware of their security problems. But too few actively take care of the solution.
Particular caution is required when using collaboration tools: software such as Microsoft Teams enables the simple exchange of messages and files. It’s a cloud-based team collaboration software that is part of the Microsoft 365 and Office 365 suite of applications, thus the data is sent to the cloud.
Simple solution: always remember that your business is at the mercy of cloud file attacks or that you are in the grip of data leakage. Only then you’ll take data protection into your own hands with the most important tool: encryption.
Encryption is effective when files are still encrypted on the device on which they are created or edited. In this way, the information is protected during transmission to the cloud and during the entire storage period. You can use it to ward off attacks by ransomware and protect yourself from access by the cloud provider or foreign authorities.
Encryption is a good tool for more data security. High-quality encryption software fits seamlessly into existing workflows. This additional layer of protection is also ideal for backups. Data encryption for information stored on the cloud network makes sure that even if the data is lost, stolen, or mistakenly shared, the contents are virtually useless without the encryption key as the keys are only made available to authorized users.