Physical & Cloud #DataProtection: Best Practices for your #Backup and #RecoveryProcess
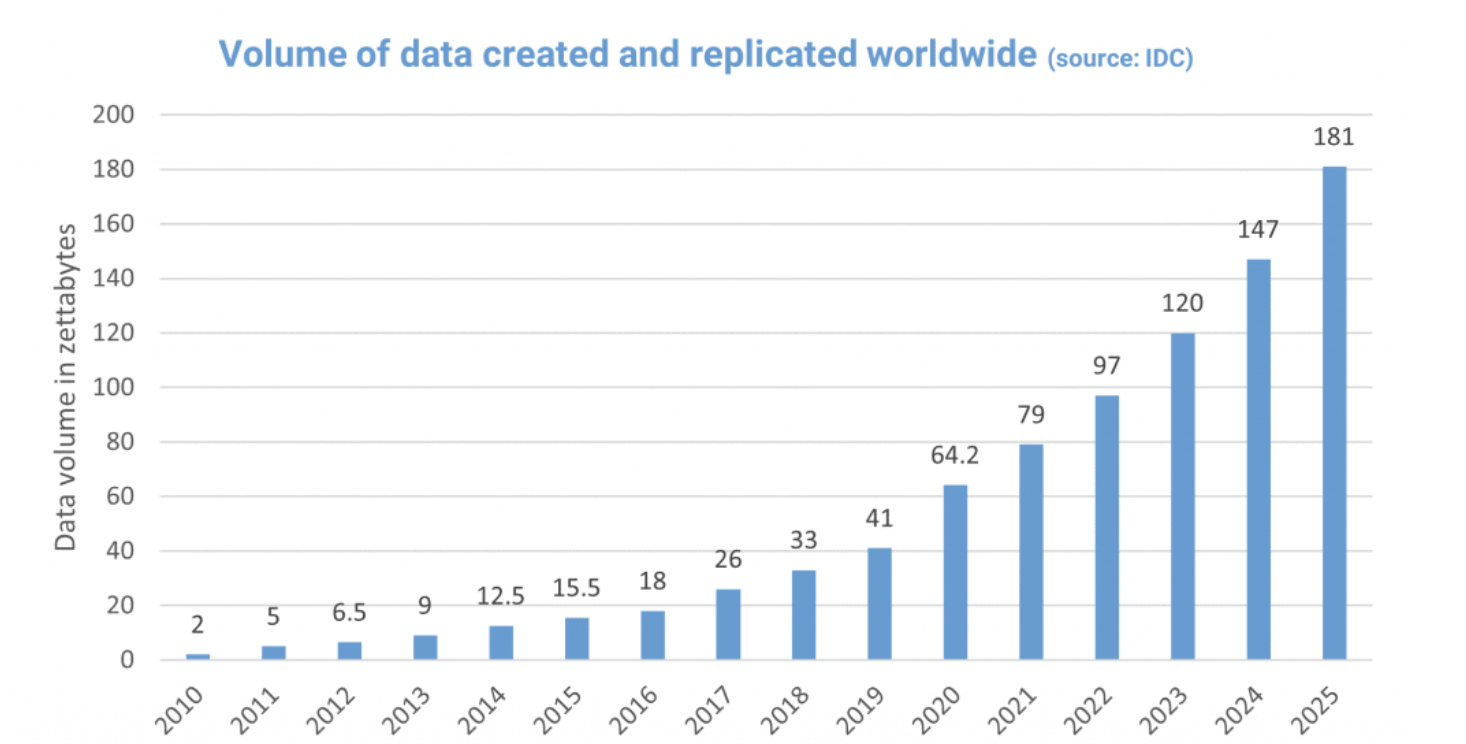
Data, one of the most valuable assets of organisations. Massive data is the new currency. Thanks to advancements in technology and connectivity, data creation is skyrocketing. According to IDC, Global DataSphere Forecast, 2021-2025, the global data creation and replication will experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23% over the forecast period, leaping to 181 zettabytes in 2025. That’s up from 64.2 zettabytes of data in 2020 which, in turn, is a tenfold increase from the 6.5 zettabytes in 2012. These data are stored in ever-increasing environments and connected devices, therefore backup and restoring the capability of an information system is a real challenge to ensure business continuity and the availability of associated data.
What must IT departments do to fulfill the data security mission? Well, the data security policy is at the heart of each business concern and should be a fundamental part of their security strategy. Planned security measures can then create tactical and operational rules through the joint efforts of security and storage teams. To this end, storage must be an integral part of the company’s security strategy.
To achieve these objectives, a company must establish a cluster around the following five essential aspects:
• Allocation of responsibilities;
• Risk Assessment;
• Development of a data protection procedure;
• Communication of data protection procedure;
• Execution and testing of the data protection procedure.
- Allocation of responsibilities
The goal is to make storage security a fully-fledged feature of the IT security architecture. Even if the company decides that the responsibility for backup or storage security rests within the storage team, it must nevertheless integrate any safety measures in this area with task to secure the rest of the infrastructure. This integration will contribute to the establishment of in-depth protection. It is also advisable to share responsibility for extremely sensitive data. It’s, therefore, better to ensure that the person authorizing access is not the same as the person responsible for enforcement.
- Assessment of storage risks in the area of IT security
#Managers must review each step of their backup methodology to identify security vulnerabilities. Can an administrator secretly make copies of backup tapes? Are they stored in boxes accessible to everyone? Is there a rigorous end-to-end monitoring chain for backup tapes? If critical data is backed up and transported, vulnerabilities of this nature could make it easy prey. If the risk analysis reveals many vulnerabilities, the company must seriously question the encryption of its data.
- Development of an information protection program that guarantees the security of company data, at all times, wherever they are
Multi-level protection should be adopted by taking existing best practices for the data network in order to apply to the storage network, while adding specific layers adapted to the characteristics of the archived data, for example:
- Authentication: application of multi-level authentication techniques and anti-spoofing (anti-identity or address spoofing).
• Authorizations: access rights according to roles and responsibilities (as opposed to total administrative access).
It is imperative to duplicate backup tapes because it is never good to depend on a single copy of the data. Despite the longevity of the bands, they are still exposed to environmental and physical damage. A common practice is to perform nightly backups and then store these off-site tapes without any verification. Recommended best practices include duplicating backup tapes and then storing offsite copies.
Magnetic tapes remain the preferred storage mode for backups because they are economical and offer sufficient capacity to back up an entire operating system on a single cartridge. When stored properly, archival tapes have a lifetime of more than 30 years, making them an exceptionally reliable storage medium.
- Communication of the procedure to be applied with regard to the protection and security of information
Once the procedure for protecting and manipulating sensitive data has been defined, it is important to ensure that those responsible for their safety are informed and trained. Safety rules are the most important aspect of assigning responsibilities. Functional managers need to be aware of risks, countermeasures, and costs.
Data loss and intellectual property theft affect the entire enterprise, not just the IT department. As such, the Director of Security must undertake a data security approach by training the different functional frameworks in the risks, threats and potential harms arising from security breaches, as well as the cost of the various possible countermeasures in this area. In this way, company executives can raise awareness about the cost/benefit of investments in data security.
- Implementation and testing of Data Protection and Security Plan
Securing data is not about technology but about the procedure. This is why it is essential to test the procedure. In addition, as the growth of the company is accompanied by an evolution in security and data protection needs, IT security practices must also evolve. Once the complete security plan has been developed, defined, and communicated to the concerned team, only then it’s the right time to implement it. IT team must ensure the implementation of the tools, technologies, and methodologies necessary for the classification of information. New technologies may be required to classify information or label it with metadata so that it is backed up according to appropriate rules and procedures.
Once in place, the procedure must be tested, both concerning backup and restore. The test is to introduce, into the process, any possible and imaginable danger, whether it is the loss of a tape or a server, network problems, equipment or filing of data or any other scenario which could affect the company’s performance.
It is advisable to carry out tests with personnel who are less familiar with the procedure, to ensure that it can nevertheless be applied without difficulty in the absence of the usual supervisor (due to illness, holidays or departure).

