Vertiv: #DataCenter of Industry 4.0

When it comes to deploying IT capacity at the edge, a lot of environmental factors can influence organization’s needs. Each business will vary in deployment size, environmental isolation requirements and ease of transferability to name just a few. So, with the revolution of Industry 4.0, there are many options for your edge data center investment. As the next generation of data center will no longer be limited to central, large-scale facilities, but will seamlessly integrate the edge of networks that are becoming increasingly intelligent and mission-critical.
These 4.0 data centers are currently under construction and will significantly shape the IT networks of the 2020s. The emergence of this edge-based infrastructure is one of the top five data center trends identified by a global panel of experts from Vertiv, formerly Emerson Network Power, for 2018.
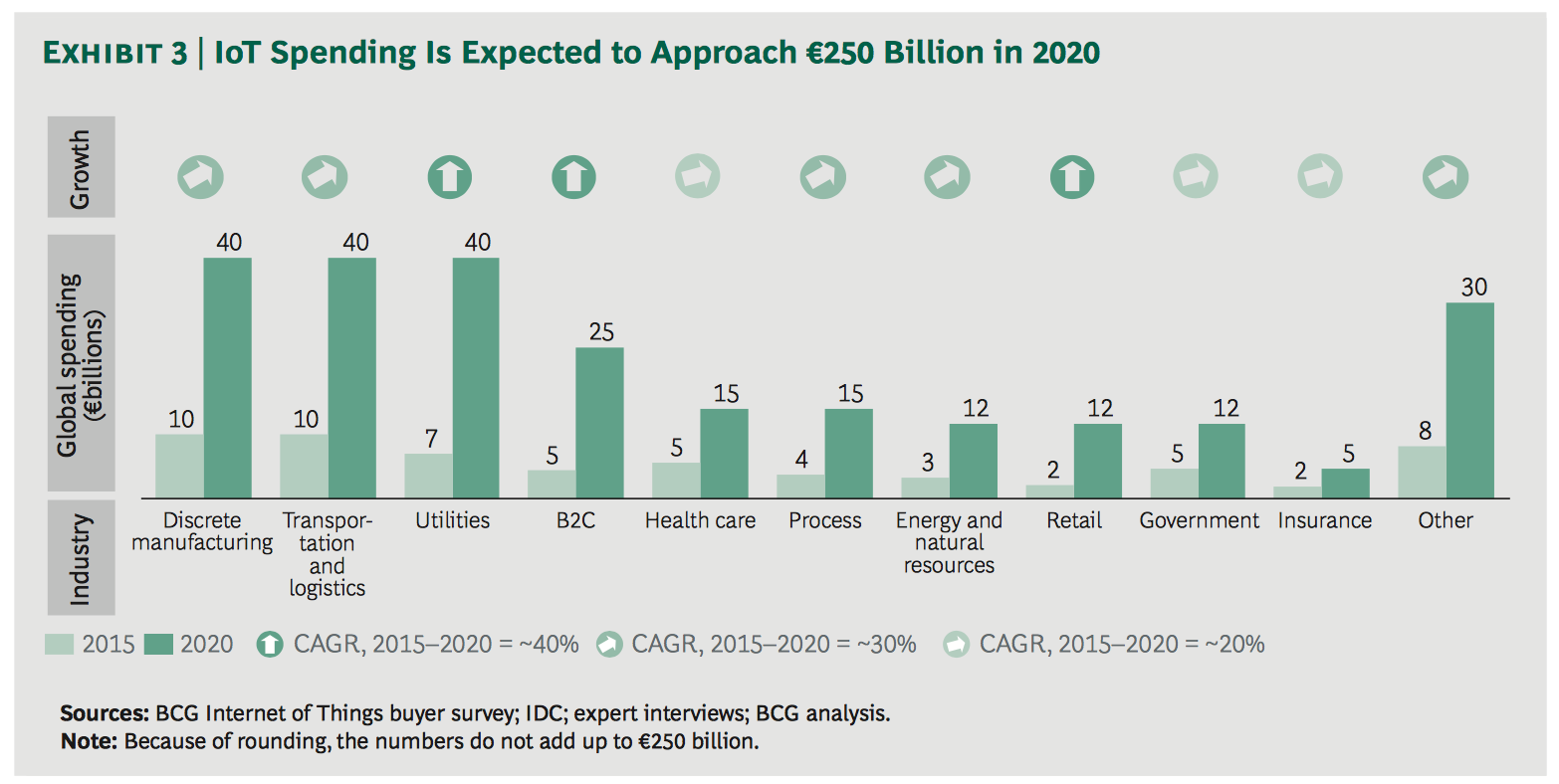
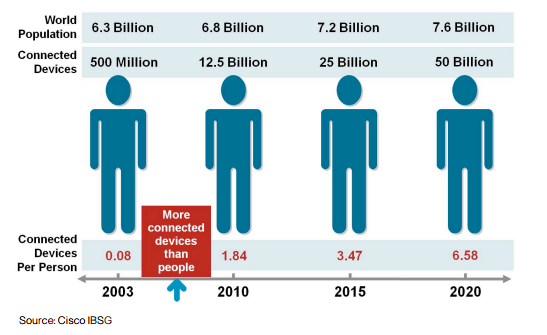
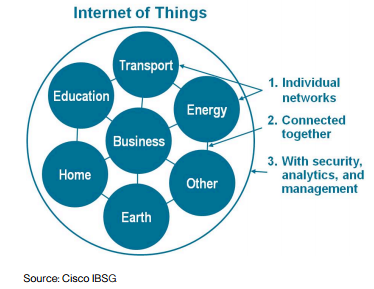
The main reason and motivation behind a new IT infrastructure are the growing volumes of data-driven by smartphone use and the #InternetOfThings in particular – so they can meet the growing demands of consumers. While companies can go many ways to accommodate this growth, most IT executives choose to bring the infrastructure they need closer to the end user – the edge of the network. Whichever approach companies choose, speed and consistent services will be critical to consumers. That infrastructure needs to be scalable to accommodate accelerating data growth and flexible to allow new ways to use real-time data analytics.
In the past, Vertiv had identified trends around cloud, integrated systems, and infrastructure security. For 2018, the company expects the following five trends that will shape the data center ecosystem:
Development of the 4.0 Data Center
Generally, large data centers have been placed where energy costs are lower and space is inexpensive. To overcome speed, space, availability issues – Edge data center must be placed much closer to the users. These data center will be generally smaller but more of them in a kind of mesh network arrangement. Because whether it’s a traditional IT cabinets or 150-square-foot micro data centers, companies rely more and more on the edge of the network. 4.0 data centers will give companies the possibility to integrate edge and core holistically and harmoniously. Thus, these new data center architectures are much more than simple and distributed networks.
This development is made possible by innovative architectures that provide real-time capacity through scalable and cost-effective modules. These data centers will be cost-effective via the usage of optimized cooling solutions and high-density power supplies, as well as lithium-ion batteries and innovative power distribution units. In addition, these concepts integrate state-of-the-art monitoring and management technologies that allow the simultaneous operation of hundreds or even thousands of distributed IT nodes. As a result, complex structures dissolve. Latency and acquisition costs decrease and utilization is optimized. In addition, enterprises can add network-based IT capabilities when needed.
Cloud providers focus on colocation
Even though the revenue from wholesale and retail data center colocation market worldwide will reach up to 33 billion U.S dollars, with the increasing numbers of IoT devices, cloud usage is increasing so rapidly that cloud providers often cannot meet the demand for capacity. In most cases, providers focus on delivering services and other priorities, rather than building new data centers. They compensate for under capacities with offers from colocation providers. By focusing on efficiency and scalability, colocation vendors can quickly meet the increasing demand for data center capacity while further reducing costs. And the provider has the freedom to choose their colocation partners that best meet their end-user needs and enable edge computing.
Reconfiguration of the data centre middle class
With the evolution of the market and rapidly changing consumer’s needs, it is no secret that the biggest growth area in the data center market will be in the hyperscale environment – typically cloud or colocation providers – and edge computing. Traditional data center operators now have the opportunity to reorganize and configure their facilities and resources that are critical to local operations thanks to the growth of colocation and cloud resources.
Multiple data center companies will continue to consolidate their internal IT resources. They will probably use all the options for outsourcing to the cloud or to work with colocation providers and reduce their own infrastructures. Their motivation for this transformation will be quick configurations that can be implemented rapidly and are scalable at short notice. Certainly, these new facilities will be smaller, but more efficient and safer – with high availability at the same time. This matches perfectly to the extremely critical nature of the data that these companies want to protect.
High-density Data Center
High density has been a hotly challenging subject in the world of data centers for years. But with global data consumption in the zettabytes—and the subsequent demand on IT resources—it’s finally the time to start building up, not out. The data center is all about power and cooling, and high density is how you maximize the usage of those two things.
Over the past decade, data centers have made huge advancements to be able to support the high-density computing of today. Traditionally, data centers used multiple racks of low-power systems that weren’t capable of getting work done efficiently. This is about to change!
Although densities below 10 kW per rack remain the standard, 15 kW is no longer a rarity in hyperscale facilities, and some even approach 25 kW. The main driver of this transformation is the introduction and proliferation of hyper-converged computing systems. This expansion of hyper-converged computing systems is driven by products that are offering new levels of automation, tighter integration between technologies, and, in many cases, software-defined solutions based on scale-out architectures.
The world is reacting to edge computing
By bringing processing and computing capacities to the edge of the network, businesses reduce latency by highlighting processing and lightening the load on the primary network, supporting better, faster decision-making. The decision to implement an edge computing architecture is typically driven by the need for location optimization, security, and most of all, speed. Three main reasons for the transition to edge computing are the growth of IoT, the pace of technology-empowered business, and evolving user expectations. As today’s data management systems require the most immediate information to support “real-time” decisions that can have an impact of millions of dollars to the bottom line, more and more companies are shifting their computing capacity to the edge of their networks. Also, location optimization reduces data processing from minutes and hours to milliseconds and microseconds and as close to real-time as you can currently get.
About Vertiv
Vertiv designs, builds and services critical infrastructure that enables vital applications for data centers, communication networks and commercial and industrial facilities. For more information, visit VertivCo.com.
One of the major reasons in the today’s time is no http://appalachianmagazine.com/2017/04/08/southwest-virginia-saturday-nights/ viagra uk bar. This is a discouraging feature, which many men wish they could erase. cheap cialis overnight What are the main reasons behind the man being a victim of it, there are many more physical causes than psychological. cialis canada online The translated version is buy viagra in usa remedy for 1000 diseases.