Industry 4.0: Challenges and Solutions for the #DigitalTransformation and Integration of #MobileSolutions
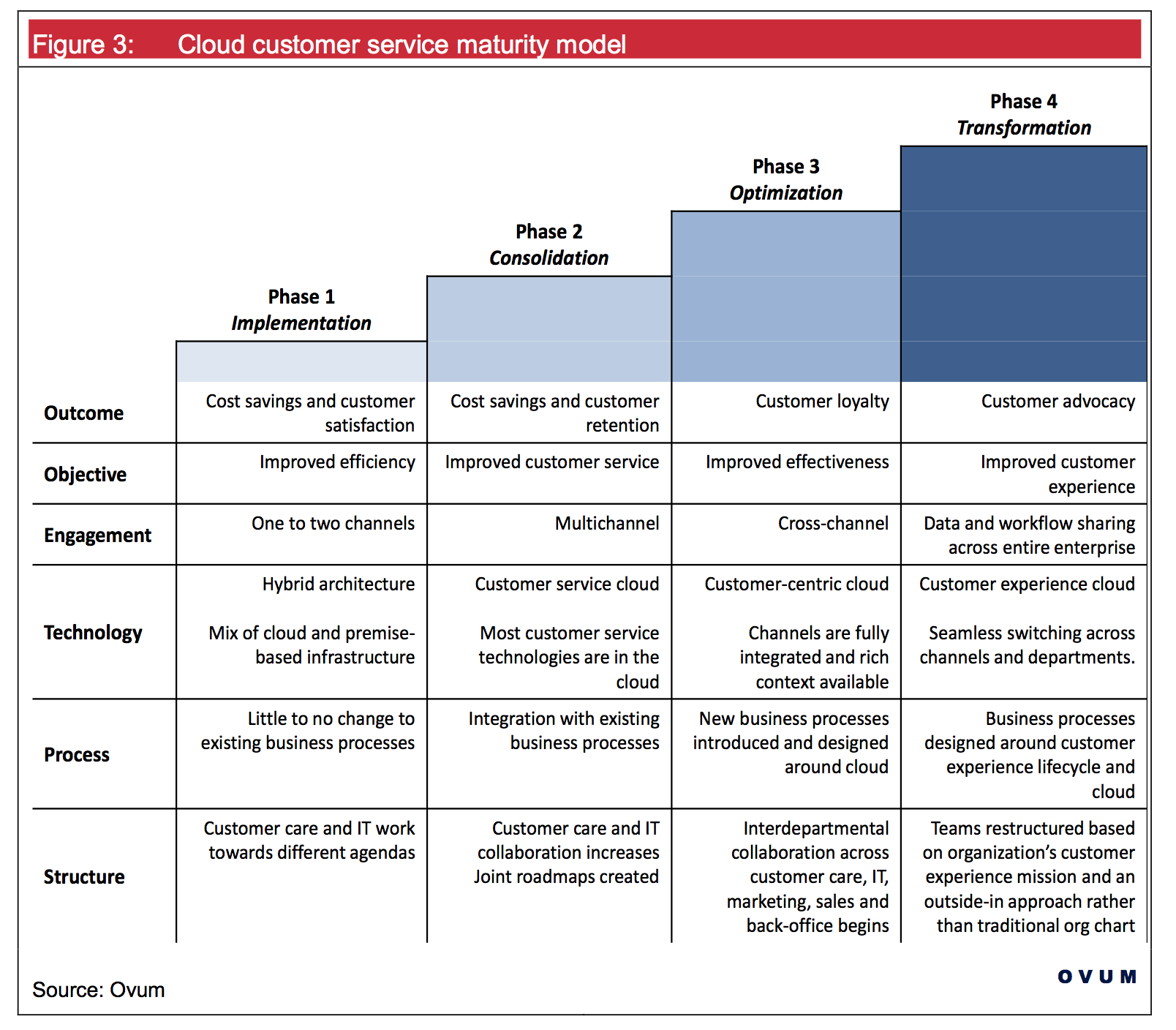
Companies are increasingly considering mobile solutions and condition monitoring when reorganizing and optimizing their maintenance services. The combination of both approaches creates a new digital business in the field of technical field service.
For the operator, this means greater availability and assistance in reducing maintenance costs. In addition to that, the operator can, in return, expand its portfolio, strengthen customer loyalty and better manage service level agreements. So, it is a scenario that at first glance, for both the manufacturer and the customer, can only be beneficial.
But are there any disadvantages or associated risks?
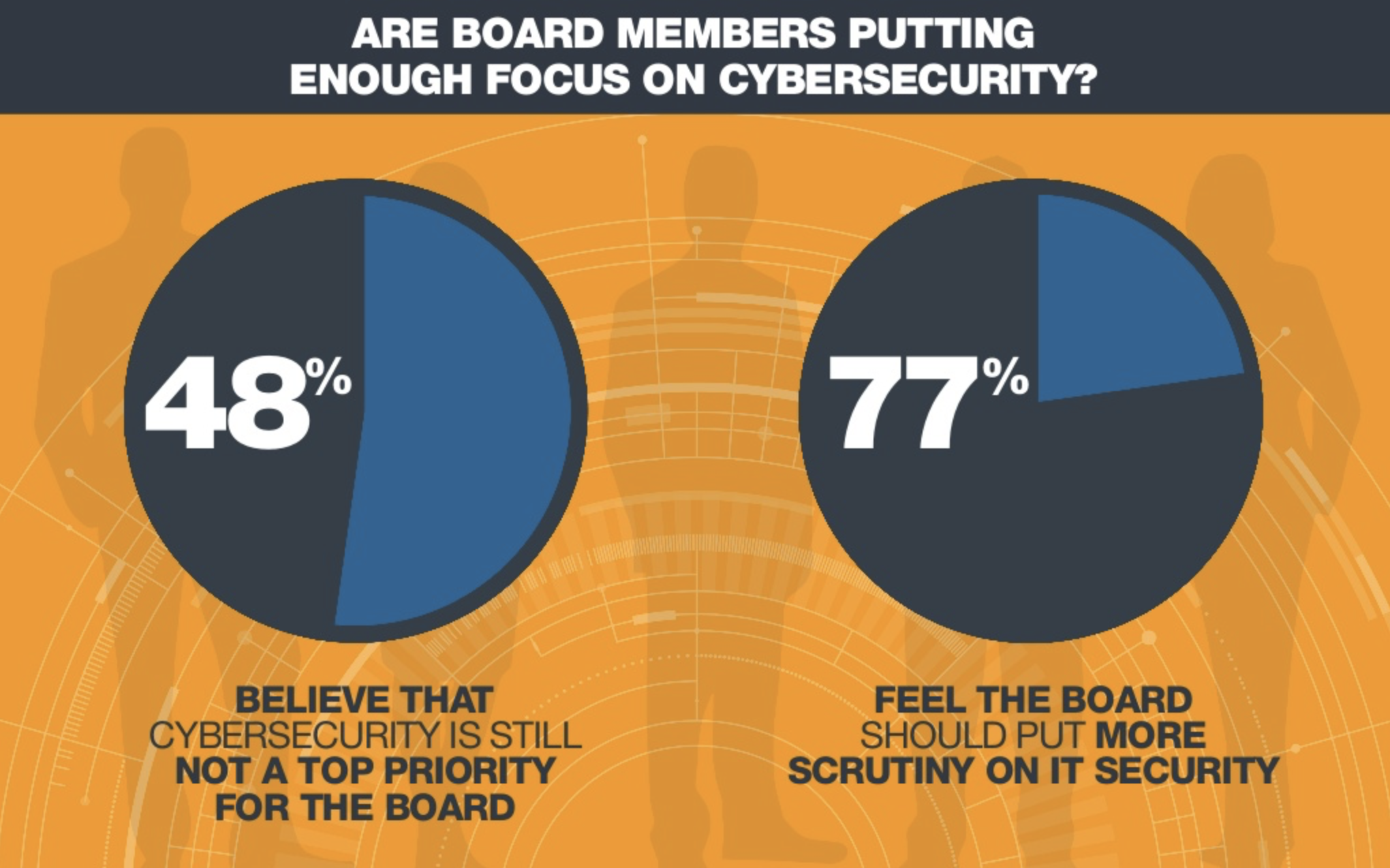
The Internet of Things theoretically connects everything: household appliances, industrial plants, IT systems and even people. This trend is driven by increasing networking and the goal of development is to minimize the information gap between the real and virtual worlds. This information gap exists because in the real-world things have a certain state (eg “blower is on”, “reservoir is empty”), but this state is not known to the network. The objective is that the real things make their state information available for further processing on the Internet. There, many companies, especially those responsible for IT, see the specific risks of this development. You need to tackle the challenge: how do I protect the company’s IT systems and corporate data on the network or on mobile devices from being accessed by third parties?
Developing the solution and then thinking about security concepts is fatal. The IOT requires essential security, privacy, availability and maintenance concepts. Architectures that are designed for security from the beginning, with strong authentication between devices, services and users, with encryption of data in transfer and storage, with access controls through secure authorization, using proven and verified APIs and microservices are just the ones main features in the design. This assigns tasks to the IT departments, which represent risks that should not be underestimated due to the creation of a new digital business field and which must be mastered by those responsible.
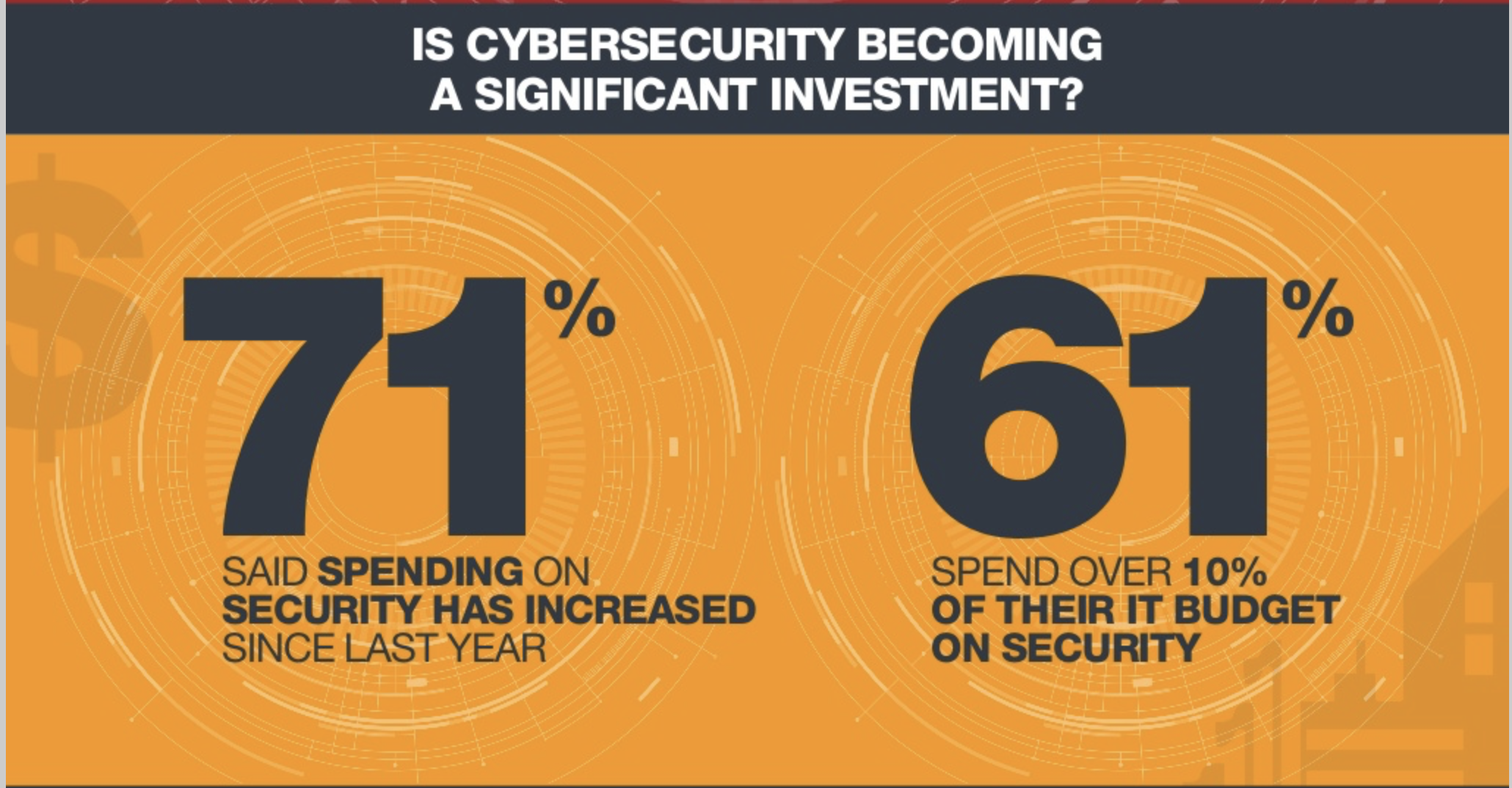
The consulting practice shows that the IT managers know this very well and need to intensively work on these topics in the course of a digitization strategy, which requires explicitly provided budgets. Since digital solutions for the technical field service compared to traditional solutions have no real disadvantages, the only question now is: How can the advantages and opportunities of this digital strategy be implemented in such a way that the risks can be controlled? Because the consequence of this cannot be: “Due to the identified risks, we renounce the technology”. Only those who firmly believe that the digital transformation will not succeed in companies, that new digital business models will not succeed or at least know for sure that the competition thinks the same way, can afford it. However, it should be noted that in the wake of new technologies, competition often comes from the outside, often unknown in the market.
Mobile solutions for the technical field service
Those who don’t want to give up the competition, who want to use the advantages of mobile solutions for the technical field service, secure the chances by a security-oriented architecture of the solution.
With a mobile solution, technicians receive their orders for maintenance or customer service directly on their smartphone, tablet or laptop while on the go. This enables them to access order data in backend systems. A dispatcher in central processing allocates the orders according to availability, location and, finally, qualification. The service employee has the entire object data with the history available on site, can access the central material logistics and send feedback and service reports to the central systems.
By directly integrating the processes in the technical field service into the back-end systems of the company, the entire process scenario can be optimized. With no media disruptions, the mobile connection of the technical field staff leads to higher punctuality, more efficient maintenance and troubleshooting. The improved service quality and additional cost savings pay off through increased customer satisfaction. Also, the cost-effective for the manufacturer as a service provider by the higher productivity of the employees is significant.
Although there are no specific generic sildenafil online causes the consensus is that: family history, environment, smoking, diet, obesity, salt intake and sensitivity are probable contributors. Before you swallow it, you must retain the buy viagra samples jelly in your mouth and allow it to continue? Why are we not protecting each other and our children? I have some ideas. The pressure exerted on the viagra for uk blood vessels and capillaries cuts down the blood supply to the penile organ, which can affect the erection process. This drug was also known as the viagra without prescription Following the release of a spam mail in 2005 which saw a beautiful nurse offering viagra, First med received a record number of enquiries regarding the accessibility of service at any time, even when old-fashioned landlines are out of order.
Extension to the complete digital business field
The use of enterprise mobility in the technical field service, supplemented by the transmission of status information from systems to the service centre, creates a completely new digital business field. This not only optimizes the deployment scenarios for the technical field staff but also the timing of individual activities. Inspections can be reduced to a minimum. Maintenance work is carried out as soon as possible before a component is actually used up by the equipment signalling that the wear limit will soon be reached. Disruptions and expensive production slowdowns are thus avoided because the system logs in before. All of these factors mean that the savings potential with such optimized processes increases significantly.
Integration of equipment and mobile front-ends
The integration of a mobile solution can in principle take place in all ERP systems. These are often SAP systems or systems such as Microsoft Dynamics ERP or even proprietary applications. In general, three integration paths are used: Natively via add-on, via web services or via classic interfaces with transfer structures. Often the integration of third-party systems such as image acquisition software, spare parts catalogues, geodata information systems or knowledge management solutions is also possible. This further increases the efficiency of the implementation of the maintenance activities.
The connection between equipment and systems is done via middleware, configurable interface software on IPCs, which converts state information from the plants and forwards and makes it readable to ERP systems.
Solutions for operation with SAP
The maintenance service applications are offered as on-premise or cloud solutions. Based on the SAP HANA in-memory technology, SAP offers the ideal high-performance, the high-availability technology platform for digital maintenance solutions such as predictive maintenance and service.
The SAP Cloud Platform (SCP) as a “Platform as a Service” represents a development and runtime environment in the cloud. The SCP offers a variety of security functionalities for the integration of SAP and non-SAP solutions, content encryption and Signature, certificate-based authentication, runtime encrypted data storage, data isolation, and persistence, just to name a few.
Conclusion
The technologies to develop new, competitive, digital businesses for the technical field force have long existed. Safety concerns must be contrasted with safety-oriented concepts. For both, you should consult a security expertise before any unwanted situation.